Filter
43
Featured
Free Access
42
Key Guidance
2
Quick Overview
1
Top Insights
1
Topics
Election Campaigns: Social Media
32
Countering Hate Speech, Disinformation & Propaganda
6
WhatsApp
3
Disinformation, Misinformation, Fake News
3
Foreign Disinformation, Foreign Information Manipulation Operations, Foreign Propaganda
3
Election Campaigns
2
Disinformation & Misinformation Law & Regulation
2
Russia: Foreign Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
2
Election Reporting
2
Election Monitoring
2
Electoral Advertising, Political Advertising
1
Digital & Social Media Use, Internet Use
1
Digital & Social Media Use: Youth
1
Disinformation Consumption & Perception
1
News Consumption & Information Sources of Media Users
1
Trust in the Media, Credibility of Media
1
Big Digital Platforms, Big Tech Companies
1
Digital & Social Media Effects
1
Content Moderation & Regulation: Social Media
1
Facebook
1
Telegram
1
Twitter & Microblogs
1
Conspiracy Narratives, Conspiracy Theories
1
Effects of Disinformation on Democracy
1
Gendered Disinformation
1
Media Literacy: Disinformation, Fake News, Hate Speech
1
Fact-Checking & Verification of Sources
1
Gender-Based Harassment, Intimidation & Violence
1
Good Practice Examples
1
China: Transnational Information Operations, International Broadcasting, Public Diplomacy
1
Media Literacy: Secondary Education
1
Media Literacy: Youth
1
Public Spheres
1
Research Methods
1
Language
Document type
Countries / Regions
Authors & Publishers
Media focus
Publication Years
Methods applied
Journals
Output Type
Nachrichten, Fake News und Wahlen
Media Perspektiven, issue 5 (2025), 10 pp.
"Voraussetzung dafür, dass (politische) Fake News Wirkung entfalten, sind gewisse Vulnerabilitätsfaktoren auf Seiten der Userinnen und User. Laut den Studien von Daunt und anderen (2023) sowie von Gupta und anderen (2023) gehören dazu zum Beispiel der Glaube an Verschwörungserzählungen, Patriot
...
“Votes will not be counted”: Indian election disinformation ads and YouTube
Access Now; Global Witness (2024), 9 pp.
Social media and mis/disinformation in electoral context in the DRC
USAID; FHI 360; Internews (2024), 57 pp.
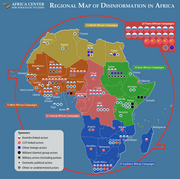
Mapping a Surge of Disinformation in Africa
Washington, DC: Africa Center for Strategic Studies, March 13 (2024)
"Disinformation campaigns have targeted every region of the continent. At least 39 African countries have been the target of a specific disinformation campaign. Disinformation tends to be concentrated. Half of the countries subjected to disinformation (20 of the 39) have been targeted three or more
...
Microtargeting, voters’ unawareness, and democracy
Journal of Law, Economics, and Organization, issue ewae002 (2024), 20 pp.
"Recent technological developments have raised concerns about threats to democracy because of their potential to distort election outcomes: (a) data-driven voter research enabling political microtargeting and (b) growing news consumption via social media and news aggregators that obfuscate the origi
...
Checking verifications during the 2022 Brazilian run-off election: How fact-checking organizations exposed falsehoods and contributed to the accuracy of the public debate
Journalism, volume 25, issue 10 (2024), pp. 2022-2043
"This study observes content-related indicators of the editorial decisions made by factcheckers during the 2022 Brazilian run-off election. Specifically, it aims to investigate factcheckers’ outputs regarding verification genres, scrutinized actors, types of verified falsehoods, and inspected plat
...
State-Sponsored Online Disinformation: Impact on Electoral Integrity in Thailand
Bangkog: Asia Centre (2023), vii, 42 pp.
"[This publication] outlines how organised disinformation campaigns or Information Operations have become the latest variable to impact the quality of elections in the kingdom [...] Drawn from past evidence, the report identifies four forms of state-sponsored disinformation campaigns that are likely
...
Eleições, direitos digitais e desinformação: Desafios e aprendizagens a partir da experiência brasileira em 2022
Derechos Digitales (2023), 128 pp.
Political Economy of Covert Influence Operations in the 2022 Philippine Elections
Top Insights
Internews (2023), 168 pp.
"This report investigates the political economy of covert influence in the 2022 Philippine Elections, with a focus on social media influencers involved in covert political campaigning. This interdisciplinary research (1) examines political influencers and peripheral actors in the field engaged in po
...
From Disinformation to Influence Operations: The Evolution of Disinformation in Three Electoral Cycles
Internews (2023), 56 pp.
"How has the Philippine disinformation landscape evolved since 2016? How different was the 2022 presidential election from previous electoral cycles? And what lessons can we learn from electoral triumphs and defeats often associated with disinformation? This report goes to the heart of these questio
...
Information Integrity to Sustain Peace during Electoral Processes. Sustaining Peace during Electoral Processes (SELECT) Project
New York: UNDP (2023), 48 pp.
"The purpose of this report is to gain a better understanding of the pertinent dynamics and to bolster the design of programming to support the information ecosystem around elections. In aid of this, UNDP sought information through a number of channels, in a review of the relevant literature, a seri
...
Survey on the impact of online disinformation and hate speech
Quick Overview
Paris: UNESCO; Ipsos (2023), 35 slides
"On average in the 16 countries surveyed, 56% of internet users frequently use social media to stay informed about current events, far ahead of television (44%). However, it is worth noting that differences exist among population groups: television is the primary source in the most developed countri
...
Regulating misleading political advertising on online platforms: An example of regulatory mercantilism in digital policy
Policy Studies, volume 45, issue 5 (2023), pp. 730–749
"Since its Joint Communication on Hybrid Threats, the EU has publicly recognized the risks to its security posed by non-traditional means aimed at undermining its legitimacy. The propagation of disinformation including misleading political advertising serves as a key example of how the Commission’
...
Dissemination of disinformation on political and electoral processes in Nigeria: An exploratory study
Cogent Arts & Humanities, volume 10, issue 2216983 (2023), 11 pp.
"Increasingly, social media has become a major source of fake news, with disinformation used as a tool in manipulating public opinion and delegitimizing opposing voices. This study explores the influence of the content of social media on traditional media, and the proliferation of disinformation in
...
Preserving trust in democracy: The Brazilian Superior Electoral Court's quest to tackle disinformation in elections
South African Journal of International Affairs, volume 30, issue 3 (2023), pp. 497-520
"Trust is the foundation on which democracy is built. Not coincidentally, it is the main victim of attacks by disinformation merchants bent on undermining the electoral process and the democratic environment. This article outlines the efforts of the Brazilian Superior Electoral Court (TSE) to tackle
...
Towards a model that measures the impact of disinformation on elections
European View, volume 22, issue 1 (2023), pp. 119-130
"Disinformation represents a danger to the integrity and legitimacy of the electoral process. From our research based on the 2021 Czech parliamentary elections, we introduce a model for measuring the resilience of citizens to disinformation. This model is then used to draw conclusions about the impa
...
Exploring Disinformation in Fragile States: Iraq as a Case Study of Influence of International Political Actors
Tokyo: Toda Peace Institute (2023), 18 pp.
"This paper examines the influence of international political actors in perpetuating disinformation in fragile states, using Iraq as a case study. The advent of modern technology and social media has transformed the global information landscape, providing new avenues for the dissemination of disinfo
...
Parallel Public Spheres: Influence Operations in the 2022 Philippine Elections
Politics and Public Policy Shorenstein Center on Media; Internews (2022), 52 pp.
"This report examines the characteristics and consequences of influence operations in the 2022 presidential election in the Philippines. The report makes three main claims: a) the term "influence operations" provides a broader frame to identify personalities, platforms, and practices that hack publi
...
Secuencia didáctica de alfabetización mediática informacional para nivel medio: Combatir la desinformación electoral y promover la participación de los jóvenes en América Latina y el Caribe
Montevideo: UNESCO (2022), 35 pp.
"En este documento presentamos una secuencia didáctica para que las y los docentes trabajen en el aula sobre las desinformaciones en contextos electorales teniendo en cuenta que las y los adolescentes son parte fundamental de los debates públicos e incluso en varios países pueden ejercer el derec
...
Conteúdo nocivo: A Meta protege a integridade eleitoral no Brasil?
NetLab; Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) (2022), 12 pp.
"Analisamos uma amostra do conteúdo denunciado ao TSE, a fim de verificar se, de fato, a Meta removeu ou indicou a presença de desinformação nestas publicações. Os resultados apontam que parcelas expressivas das publicações denunciadas e já diagnosticadas como nocivas por checadores de fato
...